ANB033 — Celiac Disease
Phase 1b cohort in celiac disease initiated; top-line Phase 1b data Q4 2026
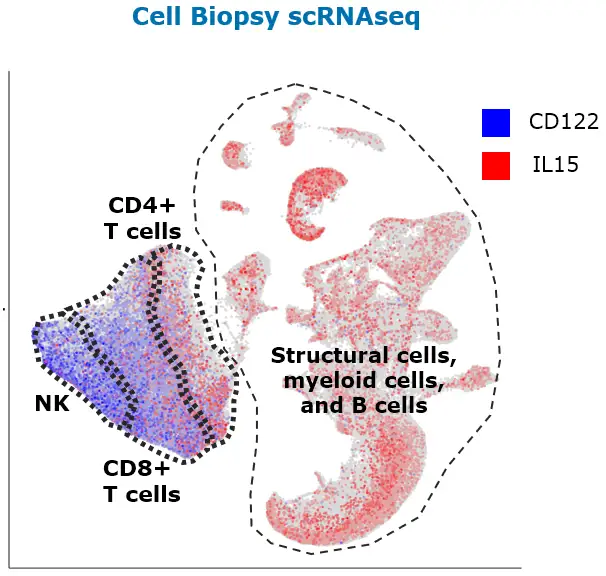
CeD is characterized by a dense infiltration of inflammatory CD122+ immune cells
Dense CD122 expression by infiltrating immune cells
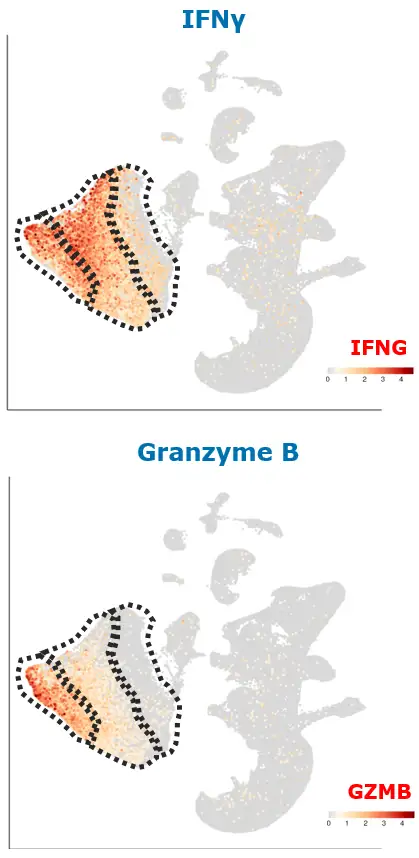
- IFNγ expression: cytotoxic CD8+ T cells, CD4+ T cells, NK cells
- Granzyme B expression: CD8+ T cells, NK cells
CD122+ cells are increased 50-150% compared to healthy Broad IL15 expression by structural cells
- Epithelial cells, myeloid cells and lymphocytes
Richards et al, Cell Rep. 2025 Jul 21;44(8):116039; UMAP of single-cell RNA-seq data from celiac disease (CeD) intestine, colored by co-expression of gene pairs: Expression values are SCTransform-normalized; a color scale is used: red or blue: high gene expression, gray = low expression.
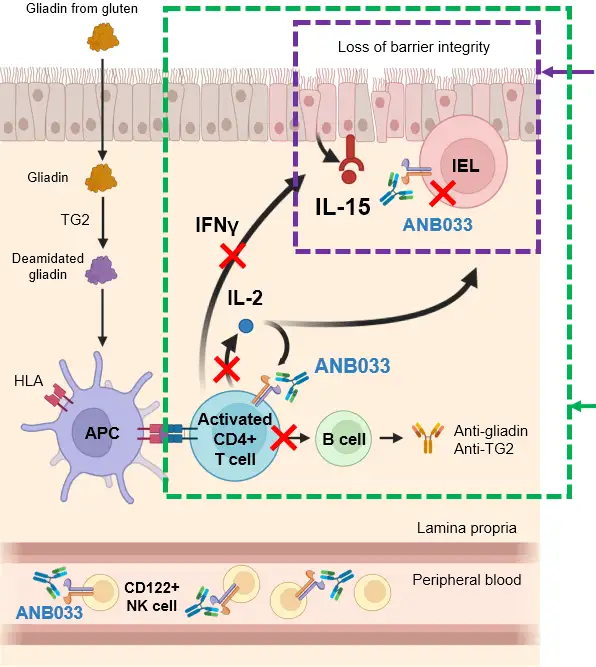
ANB033’s MOA ideal fit for targeting CeD inflammation
CeD marked by excessive IL-15 and IL-2 production which perpetuates disease
Inhibition of IL-15 signaling
- IL-15 induces proliferation of IELs
- Majority of IELs are CD122+ T cells
- Inhibiting IL-15 signaling reduces IELs
- Reduces epithelial cell destruction
- Restores barrier integrity
Inhibition of IL-2 signaling
- IL-2 stimulates
- CD4 effector memory T cell activation and proliferation
- IFNγ production leading to IL-15 secretion
- Inhibiting IL-2 signaling reduces
- Gluten-responsive CD4 T cell expansion
- Inflammatory cytokine secretion
- Downstream B cell-mediated antibody responses
Adapted from Dieckman et al. (2022) Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 66:102268.
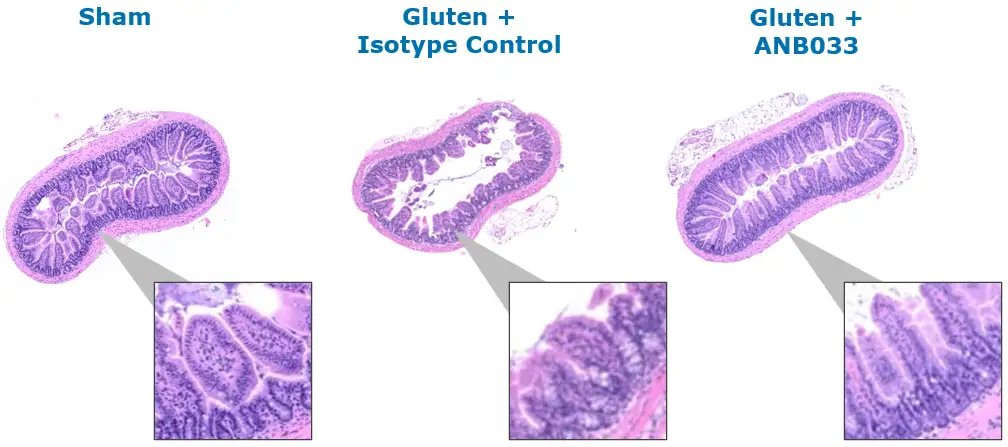
ANB033 prevents key CeD histologic manifestation of gluten-induced villous atrophy
Note: HuDQ8-Dd-villin-IL-15tg mice on a gluten-free diet are challenged with gluten, and CeD features are analyzed on day 30. The treatment regimen includes a sham (no gluten), isotype control and ANB033 surrogate antibody (anti-mouse CD122 antibody with similar epitope and affinity to ANB033) administered at 10 mg/kg BIW.
To access scientific publications on this topic, please click here.