Rosnilimab — Overview
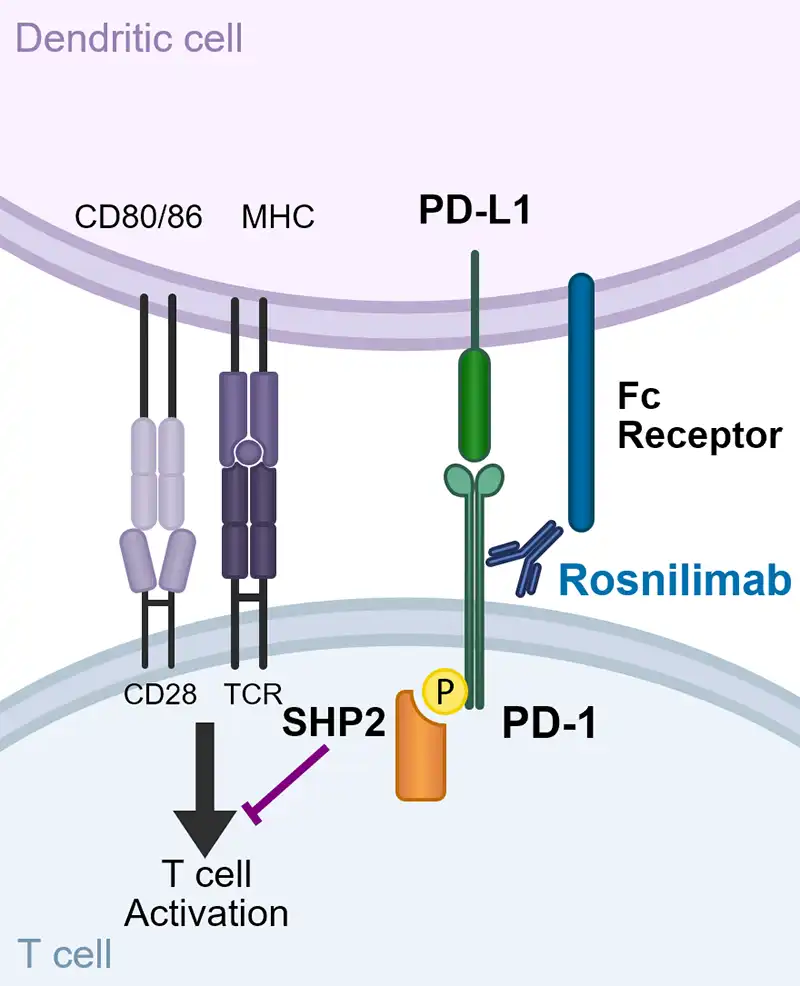
Rosnilimab is a novel PD-1 depleter and agonist that reduces overactive T cell inflammation
It has two distinct mechanisms of action, depletion and agonism, prevalent both in inflamed tissue and the periphery, targeting PD-1+ T cells broadly impacting multiple drivers of disease pathogenesis
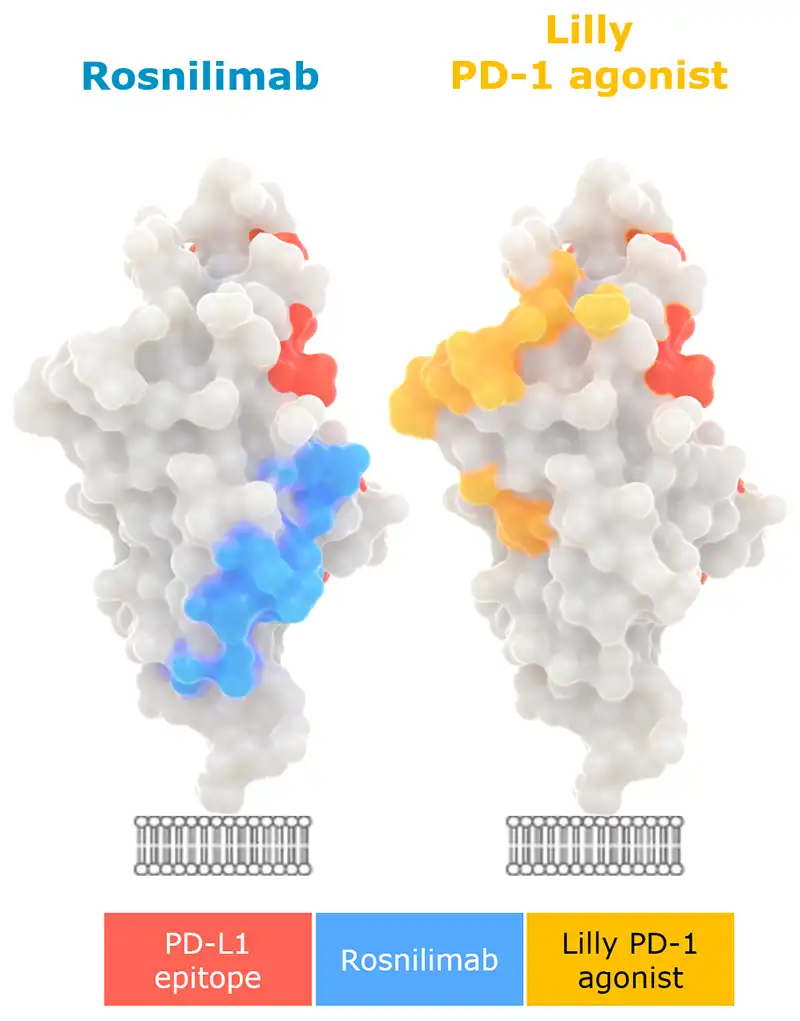
Rosnilimab optimizes PD-1+ T cell inhibitory signaling by enabling tight immune synapse formation
“A shared feature of agonist mAbs is recognition of the membrane-proximal extracellular region…” and “…activity depends on Fc receptor–supported crosslinking” -Suzuki, et al. 2023
Parmley S, et al. ECCO 2024. February 2024.
1. Adapted from Suzuki et al., Sci. Immunol. 8, eadd4947 (2023).
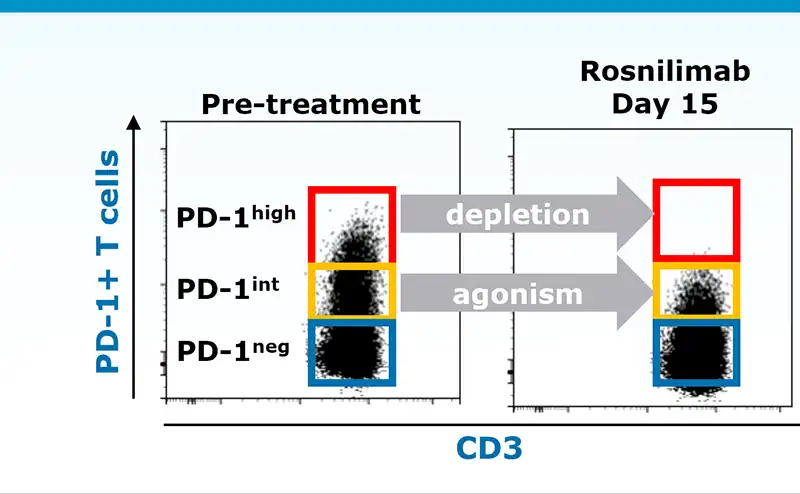
Rosnilimab restores immune balance bringing T cell composition to a less activated state
PD-1 expression on both CD4 and CD8 T cells correlates with activation state
Rosnilimab targets only a small proportion of T cells
In healthy volunteers:
- Deplete PD-1high T cells: ~5-8% of total T cells
- Agonize remaining PD-1int T cells: ~15% of total T cells
Data illustrative, Luu K, et al. ACR 2023. November 2023
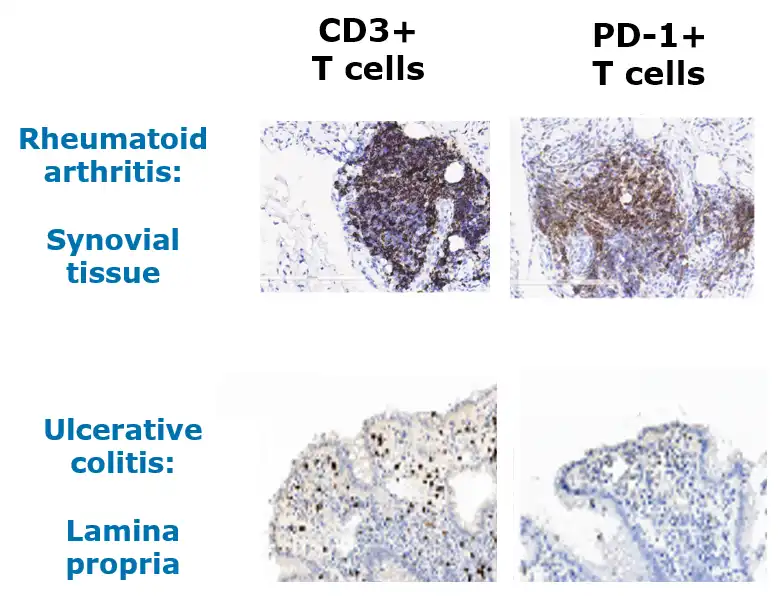
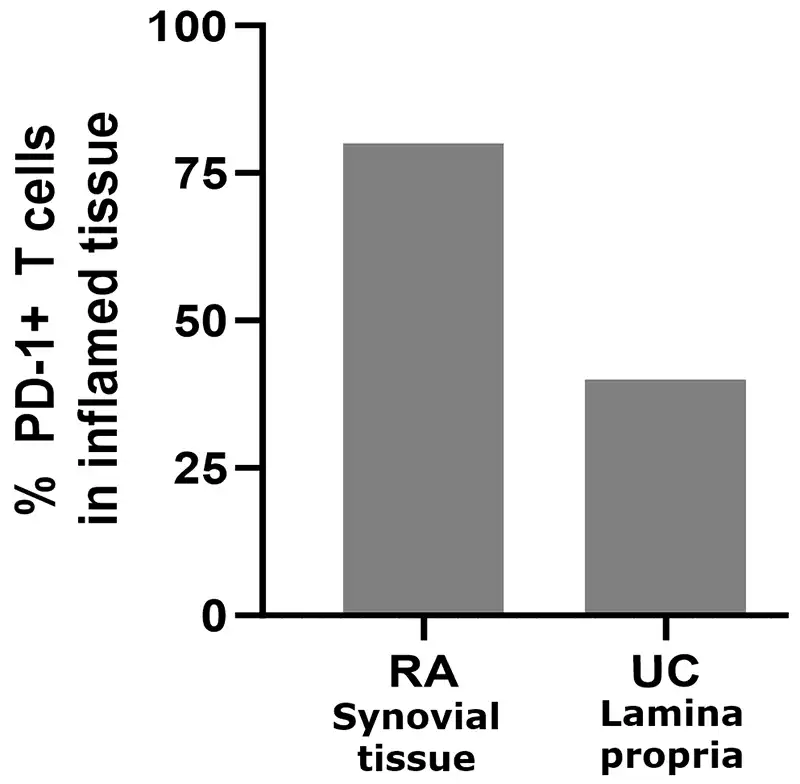
PD-1+ T cells are prevalent in inflamed tissue and periphery in RA and UC
In systemic inflammatory diseases, a multiple fold increase of PD-1+ T cells is observed in periphery compared to healthy controls1
- ~2x in RA
- ~2x in UC
Adapted from Nguyen et al, Human Pathology (2022) 126, 19e27; Guo et al, PLoS One 2018; 13(2). Roosenboom et al, Scand J of Gastro. 2021; 56(6):671-679. 1. Murray-Brown et al, RMC Open, 2022. Shi et al. (2023), PeerJ, DOI 10.7717/peerj.15481.
To access scientific publications on this topic, please click here.