Rosnilimab — Ulcerative Colitis
In Q4 2023, we initiated a global Phase 2 trial of rosnilimab for the treatment of moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis
Initial data are anticipated in Q4 2025
Adapted from Gastroenterology & Hepatology Volume 18, Issue 8 August 2022.
Parmley et. al. UEGW 2024. October 2024
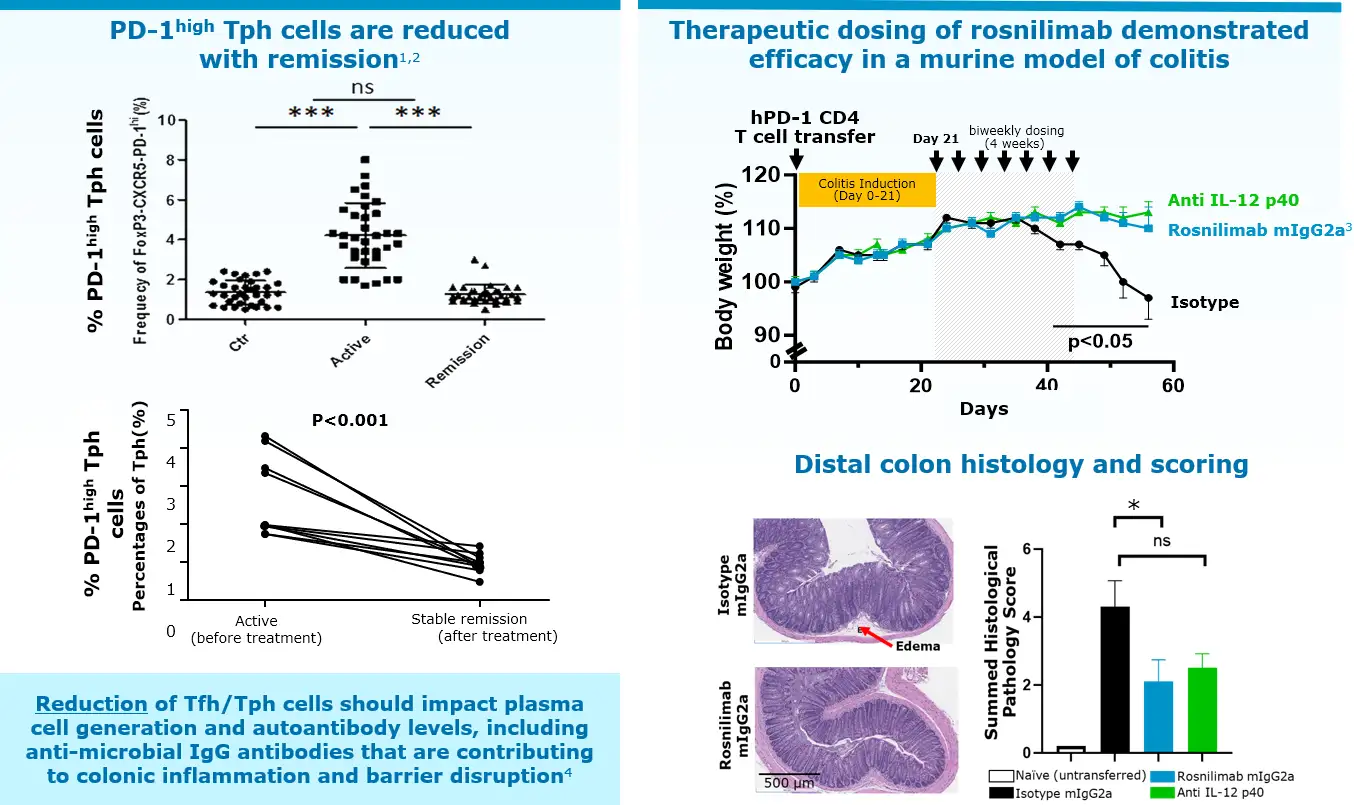
1. PD-1high Tph cells defined by CD3+CD4+CD45RA-PD-1+TIGIT+ICOS+CXCR5-. Long et al, Immunology Letters 233 (2021) 2-10.
2. Rao et al, Nature, 2017. *** p<0.001, * p<0.05
3. Rosnilimab formatted to mIgG2a to mediate effector function in mice. Suzuki et al., Sci. Immunol. 8, eadd4947 (2023).
4. Uzzan et al, Nature, 2022
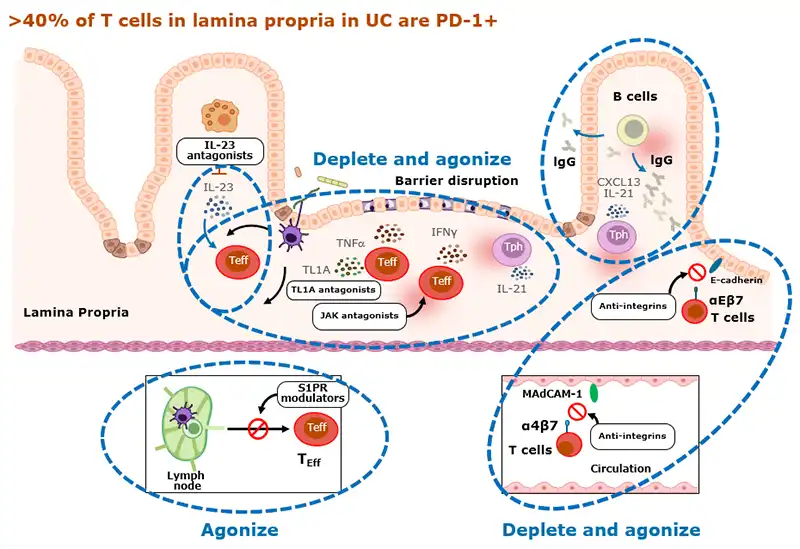
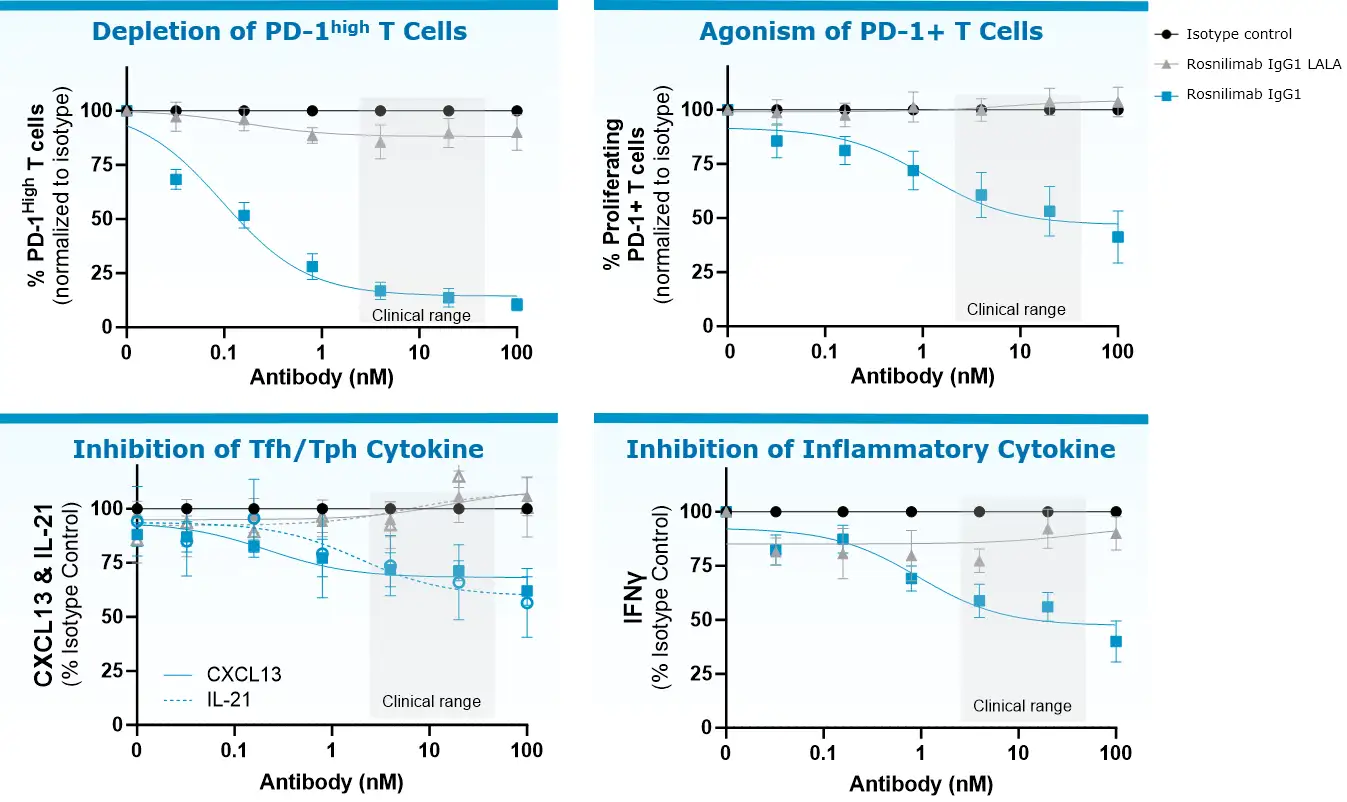
Rosnilimab’s potent depletion and agonism reduces T cell proliferation and inflammatory cytokines that disrupt barrier function
Parmley et. al. UEGW 2024. October 2024
Anti-CD3+ anti-CD28 stimulation of UC patient PBMCs for assessment of depletion and agonism MOA, representative data from N=6 donors.
Rosnilimab IgG1 LALA included to demonstrate importance of Fc effector function
To learn more about our clinical trial for Ulcerative Colitis please click here.